Security Simplified - SQL Injection

What is SQL Injection
SQL injection is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to interfere with the queries that an application makes to its database. It generally allows an attacker to view data that they are not normally able to retrieve. This might include data belonging to other users, or any other data that the application itself is able to access. In many cases, an attacker can modify or delete this data, causing persistent changes to the application’s content or behavior. portswigger
Vulnerable Code Snippet (Server Side)
- Before Directly Jumping into the Vulnerable code snipped, Imagine the following database structure with the following content:
- e-commerce [Database]
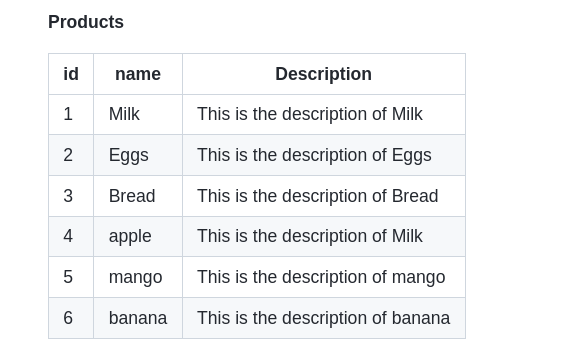
- products [Table]
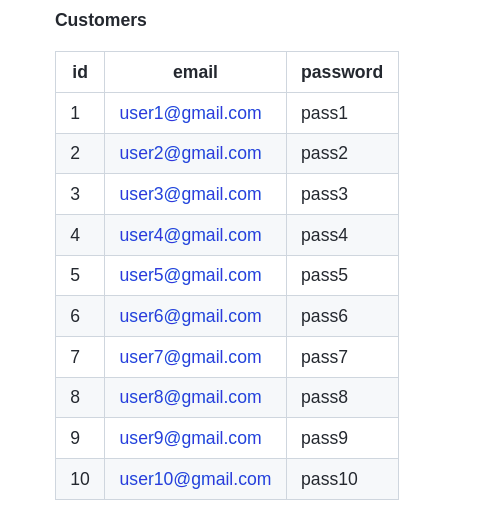
- customers [Table]
- e-commerce [Database]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
$cid=$_GET['id'];
$connection=mysqli_connect("localhost","root","","e-commerce");
$q="SELECT * FROM products where category='$cid'";
$data=mysqli_query($connection,$q);
while($pdata=mysqli_fetch_assoc($data)){
echo '<center> ';
echo '<b>Name:</b> '.$pdata['name'].'<br>';
echo '<b>Description:</b> '.$pdata['description'];
echo '<br><a href="">Order Now</a></center><br><br><br>';
}
}
?>
-
isset() is basically a function, Which checks whether a variable is set/no-empty or is not NULL.. Also check whether the variable is set/declared, If the varible is not empty it return True otherwise false.
-
$_GETis a PHP super global array which is used to access GET based Parameters from anywhere in the PHP script, As example if you visiting a URLhttps://snapsec.co?book.php?id=1, The GET basedidparameter in the URL can be accessed by the book.php by using the following code$_GET['id']. -
Then the code is creating an connection with a Mysql Server Running on
localhostwith the usernamerootand selectse-commerceas a database. -
In the next line the SQL query is dynamically generated which includes the id set by the user in the get based parameter id.
-
Lastly, The query is executed an the data is finally saved in
datavaribale. -
After that the while loop is run and all the products of the catogory of
?id=is sent to the user using theecho ""in the php
Conclusion:
So in conclusion what we understand from this code snippet is that it check if the GET Based parameter
idis set in the URL, if the theidparameter is set it then creates an connection the database and retrives the product information from product table of specific catogary and then returns the name and the description of the product to the customer.
In Browser
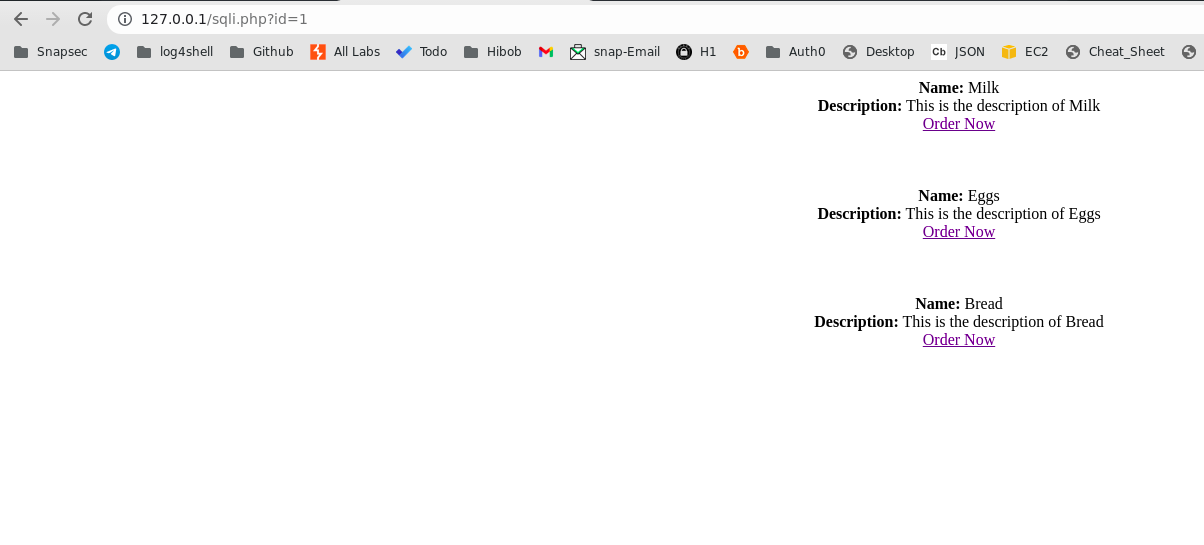
- On browsing the
sqli.php?id=1, the following query is executed, hence Returns all the products of category 11
SELECT * FROM products where category='1';
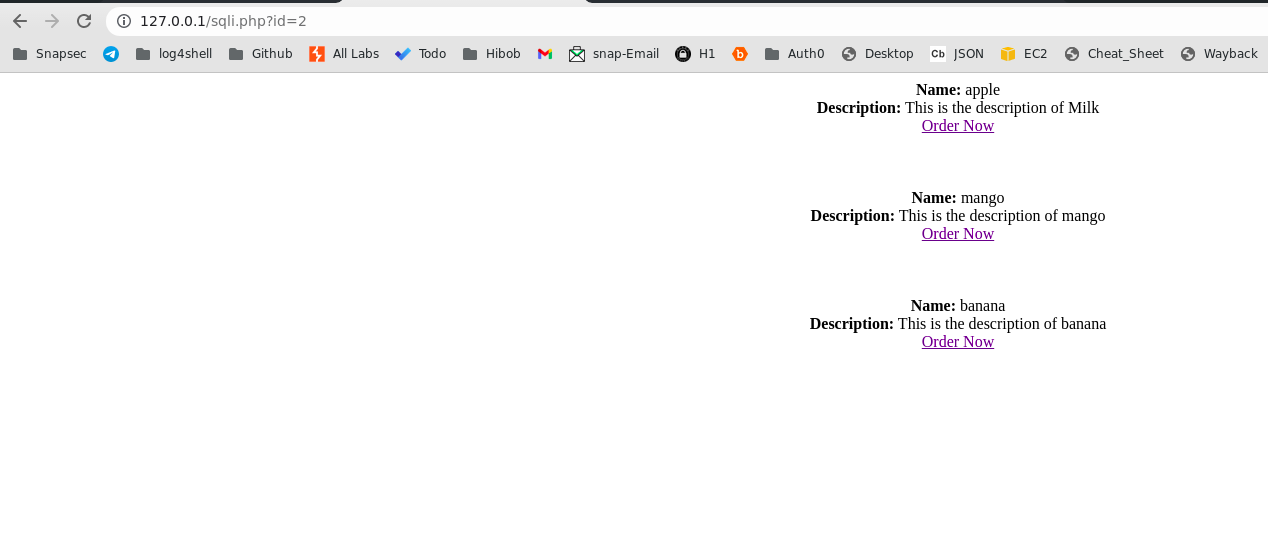
- Similarly on browsing the
sqli.php?id=2, the following query is executed:1
SELECT * FROM products where category='2';
Exploitation
We know that the mysql queries are dynamically generated in the code, therefore a user controllable input (?id=) is used to generate the query and due to the lack of proper validation on ?id= parameter, it is possible for the queries or sql statements to be injected by the attacker.
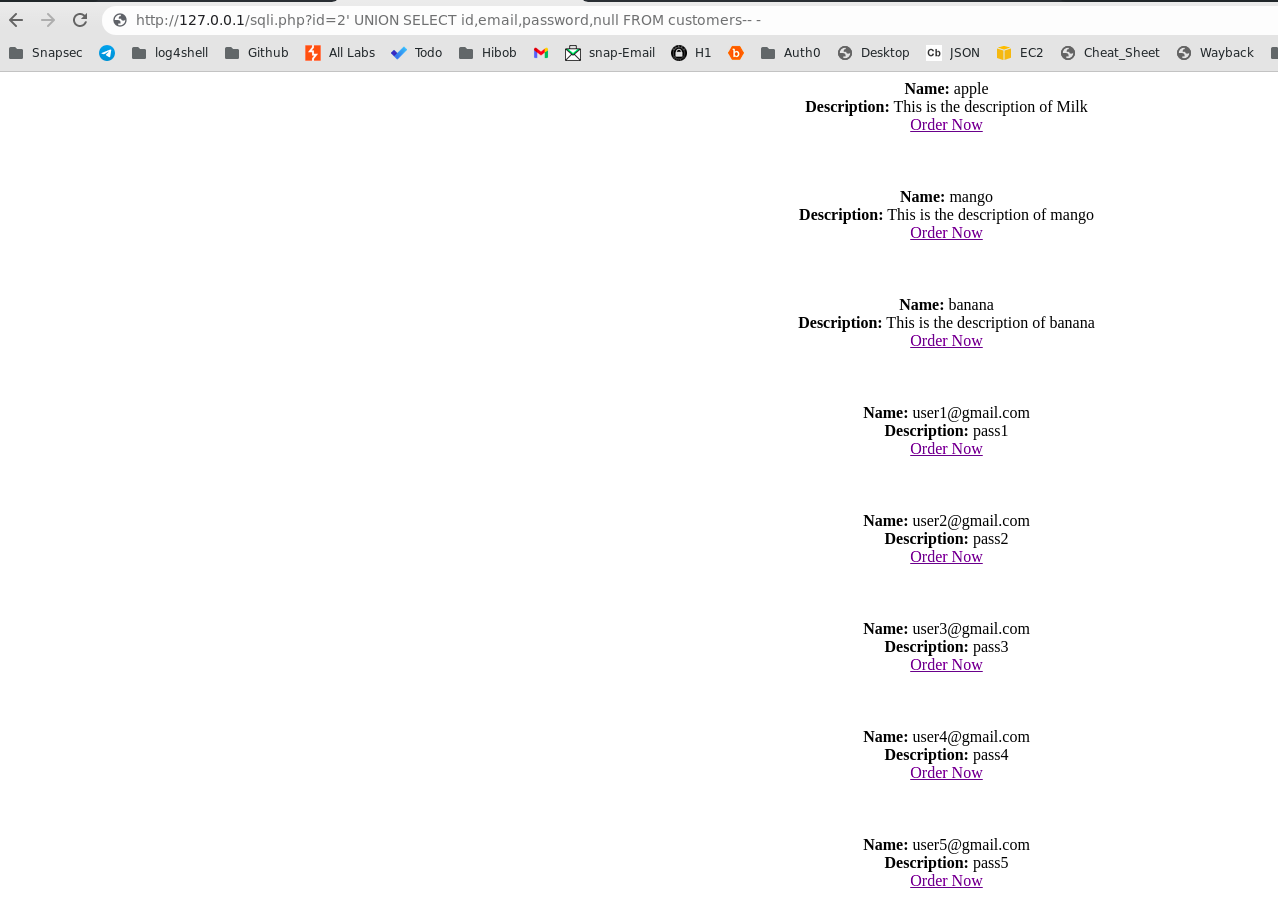
Now on visiting the following URL, In place of simple id we are adding ' UNION SELECT id,email,password,null FROM customers-- - as an value in the id parameter, Since there is not filteration or validation in place the final sql query should look like:
1
SELECT * FROM products where category='2' UNION SELECT id,email,password,null FROM customers-- -;
Since the UNION operator is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements. Our final Array($data) in the code is filled with the rows returned from the 1st and 2nd select query which is SELECT * FROM products where category='2' and SELECT id,email,password,null FROM customers hence echo’s back the customers emails and passwords on the screen. hence would allow attacker to retrive data from other tables like customers table by injecting an new SELECT statement into the query.
Where is the problem
the following part of code is responsible to generate SQL queries
1
2
3
$cid=$_GET['id'];
$connection=mysqli_connect("localhost","root","","e-commerce");
$q="SELECT * FROM products where category='$cid'";
the GET parameter id $_GET['id'] is directly taken from the user and without any validation added the query varible $q, Hence Allows attacker to escape the previous query by adding ' to the id (?id=2') and then append any MYSQL Query to the $q variable, Hence allows him to execute arbitar SQL commands on the vulnerable SERVER.
Mitigating the Issue:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
$connection=mysqli_connect("localhost","root","","e-commerce");
$cid=mysqli_real_escape_string($connection,$_GET['id']);
$q="SELECT * FROM products where category='$cid'";
$data=mysqli_query($connection,$q);
while($pdata=mysqli_fetch_assoc($data)){
echo '<center> ';
echo '<b>Name:</b> '.$pdata['name'].'<br>';
echo '<b>Description:</b> '.$pdata['description'];
echo '<br><a href="">Order Now</a></center><br><br><br>';
}
}
?>
The following code snippet introduces a new function mysqli_real_escape_string that wraps the user input id before it is passed to be a part of the dynamically generated SQL query. Ensures that special characters in a string are escaped for use in SQL statements.
Confirming the FIX
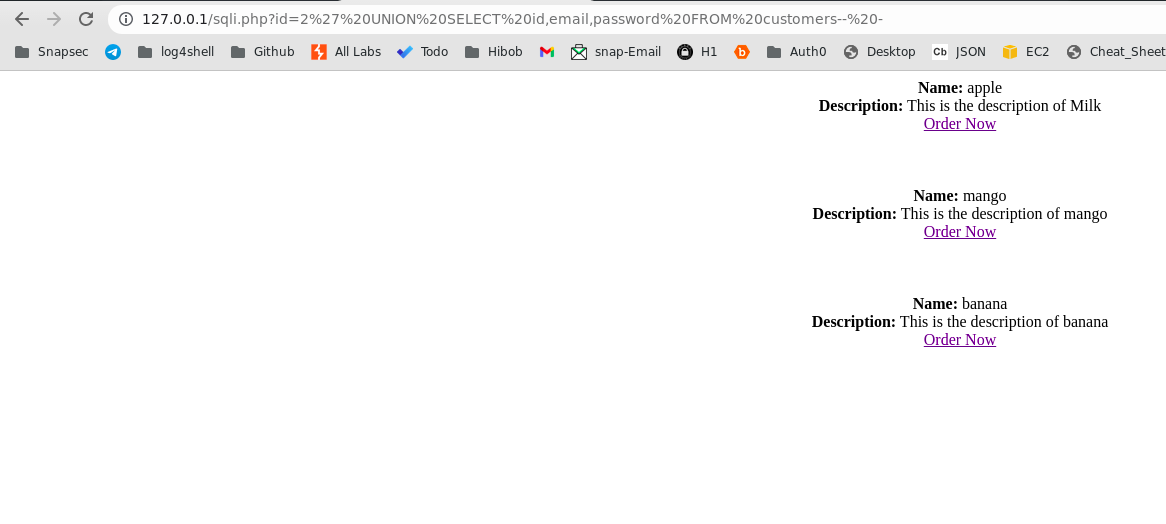
If you want to verify our fix is effective, you can check that when you add the malicious SQLi payload to the id parameter in the script, no injection attacks take place as a result of the special characters being escaped in MySQL queries. So, the final sql query should look like this.
SELECT * FROM products where category='2\' UNION SELECT id,email,password FROM customers-- -'
In the query the \ escaping slash added before ' in the user input prevents attacker from escaping the context of the id parmeter hence whole set of payload which is 2' UNION SELECT id,email,password FROM customers-- - is treated as a value of id category in the mysql query.
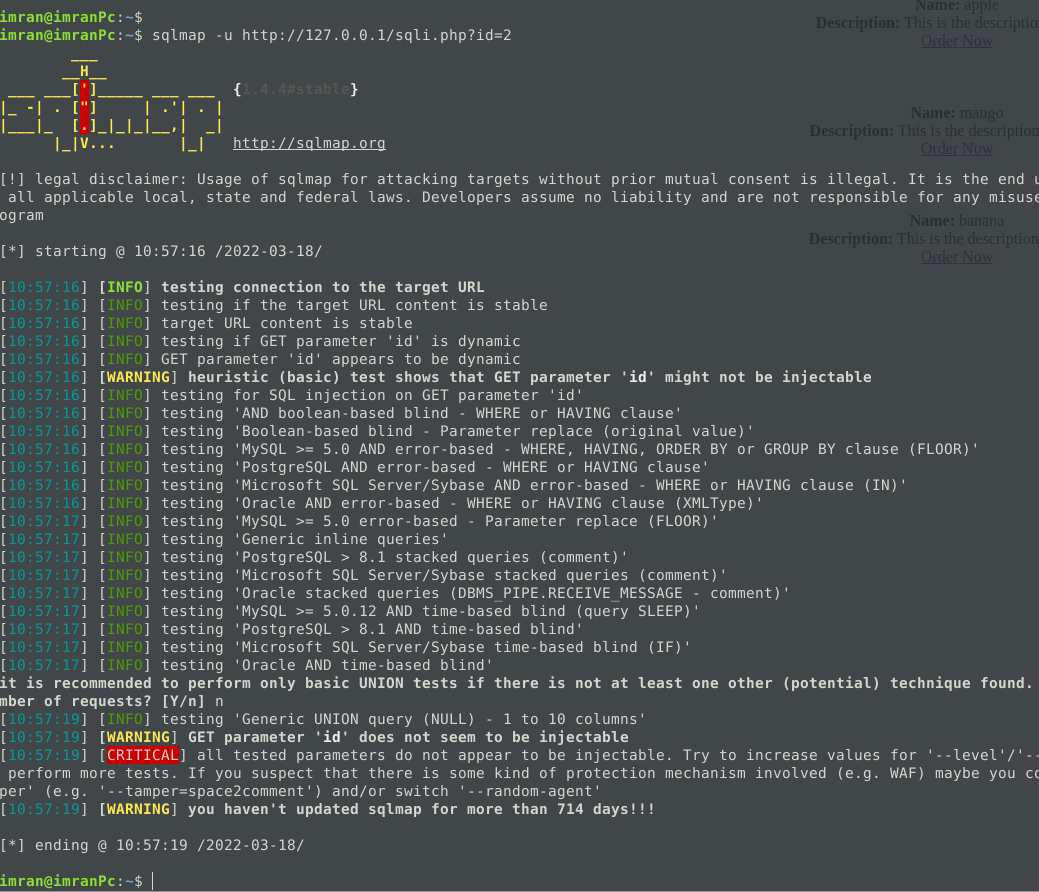
- Just to make sure none other MYSQLi exploitation techniques are working i ran a quick sqlmap scan on the script and it seems we are perfectly fine.
About us
Snapsec is a team of security experts specialized in providing pentesting and other security services to secure your online assets. We have a specialized testing methodology which ensures indepth testing of your business logic and other latest vulnerabilities.
If you are looking for a team which values your security and ensures that you are fully secure against online security threats, feel free to get in touch with us support@snapsec.co
Thanks and see you soon.
 Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter
Never miss a story from us, subscribe to our newsletter